Web technology overview
La revisió el 15:48, 16 oct 2010 per Enric (discussió | contribucions)
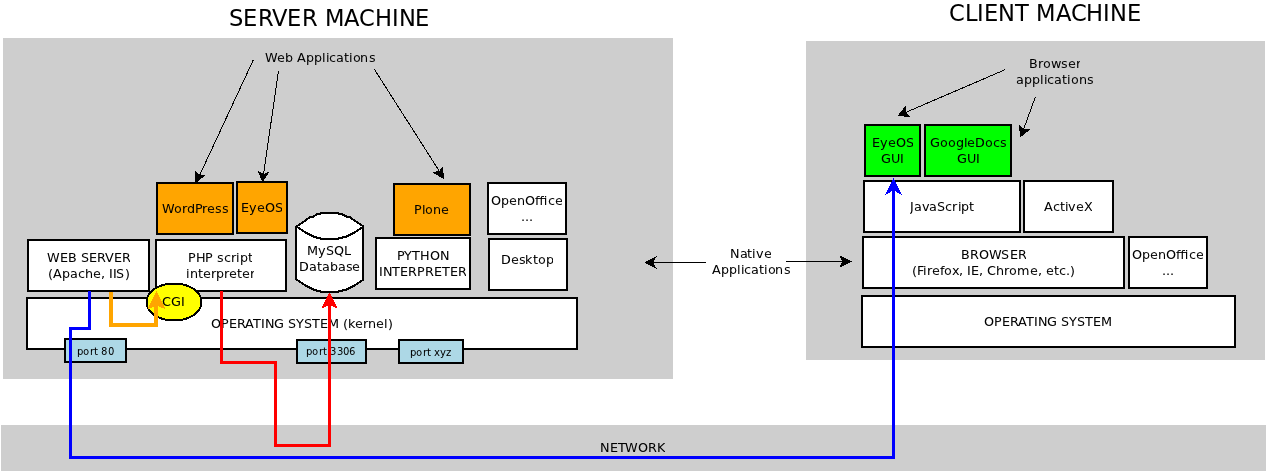
With the figure you can have an idea of how is the architecture of the Web Applications.
We highlight:
- Client-Server architecture
- Server: stores the data and processes the core application
- Client: the browser renders the graphical part a.k.a. GUI: Graphical User Interface
- Native applications (compiled) are faster in execution than scripts (interpreted by another intermediate application such as Apache).
- With Web 2.0 come the RIA: Rich Internet Applications, using JavaScript technologies.
- PHP scripting language means PHP Hypertext Preprocessor (recursive definition)
- Web applications (server-side) use to communicate to the MySQL database to store data (red line).
- Client access to web applications via port 80 of the network (blue line).
- Web server applications:
- Apache: free software web server, the more used in all the world web servers.
- IIS: Internet Information Server (Microsfot). Supports ASP.NET advanced language.
- Lighttpd: (pronunced lighty) last-generation web server used in servers with high load.
- 2 paradigms of server-side web applications:
- Script-based: Apache (web server app) executes the scripts in PHP, CGI, etc.
- Stand-alone: applications that doesn't need a web server. The usual example are applications using Python using Django framework (need a Python interpreter though). Google products are based in that technology and have better security than Apache or IIS based ones.