Diferència entre revisions de la pàgina «Web technology overview»
Salta a la navegació
Salta a la cerca
(Es crea la pàgina amb «With the figure you can have an idea of how is the architecture of the Web Applications. Imatge:web_applications.jpg We highlight: * Client-Server architecture * N…».) |
|||
| (Hi ha 2 revisions intermèdies del mateix usuari que no es mostren) | |||
| Línia 1: | Línia 1: | ||
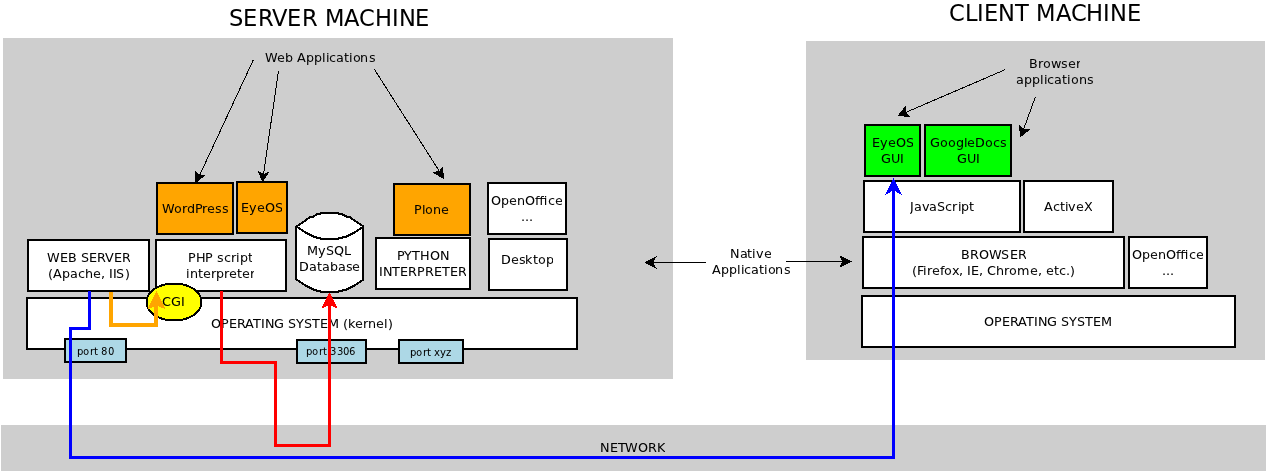
With the figure you can have an idea of how is the architecture of the Web Applications. | With the figure you can have an idea of how is the architecture of the Web Applications. | ||
| − | [[Imatge:web_applications. | + | [[Imatge:web_applications.png|920px]] |
We highlight: | We highlight: | ||
* Client-Server architecture | * Client-Server architecture | ||
| − | * Native applications are faster in execution | + | **'''Server''': stores the '''data''' and processes the '''core application''' |
| − | * | + | **'''Client''': the browser renders the graphical part a.k.a. '''GUI: Graphical User Interface''' |
| − | * With Web 2.0 the applications | + | * '''Native applications''' (compiled) are faster in execution than '''scripts''' (interpreted by another intermediate application such as Apache). |
| − | **Server-side: | + | * '''Web 1.0''' paradigm just uses '''HTML (Hypertext Markup Language)''' in client-side (server uses several programming languages as Perl or PHP). |
| − | ** | + | * With '''Web 2.0''' come the '''RIA: Rich Internet Applications''', using AJAX technologies in client-side. |
| − | * | + | * '''AJAX''' is a group of technologies that means '''Asynchronous Javascript and XML'''. Makes the client possible rich GUI applications. |
| + | * PHP scripting language means '''PHP Hypertext Preprocessor''' (recursive definition) | ||
| + | * Web applications (server-side) use to communicate to the '''MySQL database''' to store data (<span style="color:red;">red line</span>). | ||
| + | * Client access to web applications via '''port 80''' of the network (<span style="color:blue;">blue line</span>). | ||
| + | * Web server applications: | ||
| + | **'''Apache''': free software web server, the more used in all the world web servers. | ||
| + | **'''IIS''': Internet Information Server (Microsfot). Supports ASP.NET advanced language. | ||
| + | **'''Lighttpd''': (pronunced ''lighty'') last-generation web server used in servers with high load. | ||
| + | * 2 paradigms of server-side web applications: | ||
| + | **'''Script-based''': Apache (web server app) executes the scripts in PHP, CGI, etc. | ||
| + | **'''Stand-alone''': applications that doesn't need a web server. The usual example are applications using '''Python''' using Django framework (need a Python interpreter though). Google products are based in that technology and have '''better security''' than Apache or IIS based ones. | ||
Revisió de 17:38, 25 oct 2010
With the figure you can have an idea of how is the architecture of the Web Applications.
We highlight:
- Client-Server architecture
- Server: stores the data and processes the core application
- Client: the browser renders the graphical part a.k.a. GUI: Graphical User Interface
- Native applications (compiled) are faster in execution than scripts (interpreted by another intermediate application such as Apache).
- Web 1.0 paradigm just uses HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) in client-side (server uses several programming languages as Perl or PHP).
- With Web 2.0 come the RIA: Rich Internet Applications, using AJAX technologies in client-side.
- AJAX is a group of technologies that means Asynchronous Javascript and XML. Makes the client possible rich GUI applications.
- PHP scripting language means PHP Hypertext Preprocessor (recursive definition)
- Web applications (server-side) use to communicate to the MySQL database to store data (red line).
- Client access to web applications via port 80 of the network (blue line).
- Web server applications:
- Apache: free software web server, the more used in all the world web servers.
- IIS: Internet Information Server (Microsfot). Supports ASP.NET advanced language.
- Lighttpd: (pronunced lighty) last-generation web server used in servers with high load.
- 2 paradigms of server-side web applications:
- Script-based: Apache (web server app) executes the scripts in PHP, CGI, etc.
- Stand-alone: applications that doesn't need a web server. The usual example are applications using Python using Django framework (need a Python interpreter though). Google products are based in that technology and have better security than Apache or IIS based ones.