Diferència entre revisions de la pàgina «WWW History»
| Línia 12: | Línia 12: | ||
*2004 Tim O'Reilly defines '''Web 2.0 as "Web as platform"''' | *2004 Tim O'Reilly defines '''Web 2.0 as "Web as platform"''' | ||
*2005 '''AJAX''' term appears (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) | *2005 '''AJAX''' term appears (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) | ||
| + | *2009 HTML 5.0 appears. | ||
*After 2010: Web 3.0 as...? | *After 2010: Web 3.0 as...? | ||
**Semantic web | **Semantic web | ||
| Línia 19: | Línia 20: | ||
To summarize, we can say that the evolution have been really quick in the first 6 years with the introduction of client-side technologies (JavaScript, ActiveX) and the 4 version of HTML until 4.0 in 1997. | To summarize, we can say that the evolution have been really quick in the first 6 years with the introduction of client-side technologies (JavaScript, ActiveX) and the 4 version of HTML until 4.0 in 1997. | ||
From that year on, the evolution has been improving this technologies as the client-side machines has become more powerful. | From that year on, the evolution has been improving this technologies as the client-side machines has become more powerful. | ||
| − | |||
== Browsers == | == Browsers == | ||
Revisió de 13:17, 18 oct 2010
WWW = Wide World Web
Technology evolution[modifica]
- 1991 HTML 1.0 and ViolaWWW appears by Tim Barners-Lee, working at CERN
- 1994 W3C (WWW Consortium) is created by Tim Barners-Lee to standardize web languages.
- 1995 JavaScript (client-side programming language) appears in Netscape
- 1996 JScript appears in IE as a response to JavaScript
- CSS level 1 appears (by W3C)
- 1997 HTML 4.0 appears (still working in the 4.01 strict version)
- 1999 The term Web 2.0 appears
- 2000 ISO HTML = HTML 4.01 strict, and XHTML 1.0 appears
- 2004 Tim O'Reilly defines Web 2.0 as "Web as platform"
- 2005 AJAX term appears (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)
- 2009 HTML 5.0 appears.
- After 2010: Web 3.0 as...?
- Semantic web
- Computers generate content
- Metaverse: virtual and real world converge, augmented reality (SecondLife, etc.)
To summarize, we can say that the evolution have been really quick in the first 6 years with the introduction of client-side technologies (JavaScript, ActiveX) and the 4 version of HTML until 4.0 in 1997. From that year on, the evolution has been improving this technologies as the client-side machines has become more powerful.
Browsers[modifica]
The evolution of the WWW is strongly related to the evolution of the web browsers, beginning with the ViolaWWW as the first one, and following with the "war of browsers" between Netscape and MS Internet Explorer.
- 1991 ViolaWWW
- 1992 Mosaic
- 1994 Netscape Navigator: CISCO systems
- 1995 Microsoft Internet Explorer: Microsoft
- 1996 Opera
- 1998 Mozilla Internet Suite: Mozilla project replaces the Netscape project, Netscape becomes open!
- 2003 Safari: Mac OS
- 2004 Firefox: the latest trasformation of Netscape/Mozilla
- 2008 Google Chrome (and Chromium as the open version)
Browser War[modifica]
After the release of MS IE, a war between the two "mounsters" appears for the share of the browser market. New versions with lots of new features appeared at a really high rythm. As a consequence, the characteristics of this have been:
- Adding new features instead of fixing bugs
- Adding proprietary features instead of obeying standards
- Inadvertently creating security loopholes
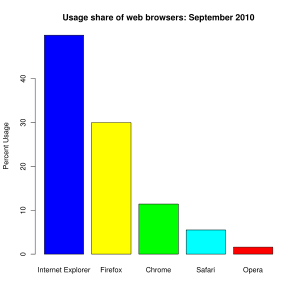
Current share of web browsers (July 2010): Complete arcticle in Wikipedia
- Internet Explorer (52.68%)
- Mozilla Firefox (30.69%)
- Google Chrome (9.80%)
- Safari (5.09%)
- Opera (1.90%)
WWW History Table[modifica]
| GML (Generalized Markup Language) is developed at IBM. Finally, SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) appears. | ||
| Web origins in CERN (Centre Européen de Recherche Nucleaire, Geneva). Tim Barners-Lee creates HTML to share graphic information of the experiences with his colleagues.
The first browser is called ViolaWWW. |
HTML 1.0 is created based on SGML style. | |
| Mosaic, the second browser is created in the NCSA (National Center for Supercomputing, USA). Improved graphics and prepared for other protocols than HTTP like FTP and Gopher.
Will be the base for later developments: Netscape and Spyglass (later buy by Microsoft and renamed Internet Explorer). |
||
| - HTML becomes an open standard.
- The W3C (Wide Word Web Consortium, w3c.org) is created by Tim Barners-Lee to standardize web languages. - Netscape Navigator appears (from CISCO). |
||
| - JavaScript language added to Netscape.
- Microsoft Internet Explorer appears. |
HTML 2.0 (+ form file upload)
JavaScript appears. | |
| - JScript added to Internet Explorer (different name to avoid trademark issues).
- Opera browser appears (commercial with trial versions). |
CSS level 1 created.
HTML (+ tables, image maps in client-side) | |
| CSS level 2
1997 January: HTML 3.2 1997 December: HTML 4.0 | ||
| Mozilla Organization founded to create Mozilla Internet Suite, a new free and open-source project for Netscape (≈ Netscape Browser code becomes free). | ||
| The term Web 2.0 appears. | CSS level 3 (current version until 2009) | |
| Opera browser becomes free of charge (with advertisements). | May: ISO HTML standard based on v4.01 strict
XHTML 1.0 (≈ HTML + XML) | |
| - Mozilla Organization becomes Mozilla Foundation due to the non-profit orientation.
- Safari Browser appears for Mac OS. |
||
| - Firefox 1.0 appears (from Mozilla Foundation).
- In the O'Reilly Media Web 2.0 Conference Tim O'Reilly defines Web 2.0 as “Web as platform”. |
||
| AJAX term created by Jesse James Garrett (Asynchronous JavaScript And XML). That term groups technologies very close to the Web 2.0 concept. | ||
| - Google Chrome for MS Windows appears, based on KHTML (Konqueror free code browser from Linux KDE).
- Chromium is the name of the open-source code used in Google Chrome. |
||
Web 3.0?
|